Products
Fast, Reliable, Everywhere

Solutions
Efficient, Innovative EV Charging Solutions.
News
We are committed to the innovation and application of EV charging.
With the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), understanding the different charging levels is becoming increasingly important. Among them, Level 3 charging stations—often called DC fast chargers—are the fastest and most powerful, making them an essential part of the growing EV infrastructure.
Level 3 chargers typically provide between 50 kW and 400 kW of power directly to an EV battery, enabling much shorter charging times compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. On average, you can recharge a mid-size EV in just 15 to 55 minutes, though costs may vary from $25 to $50 per session, depending on your location and payment model.
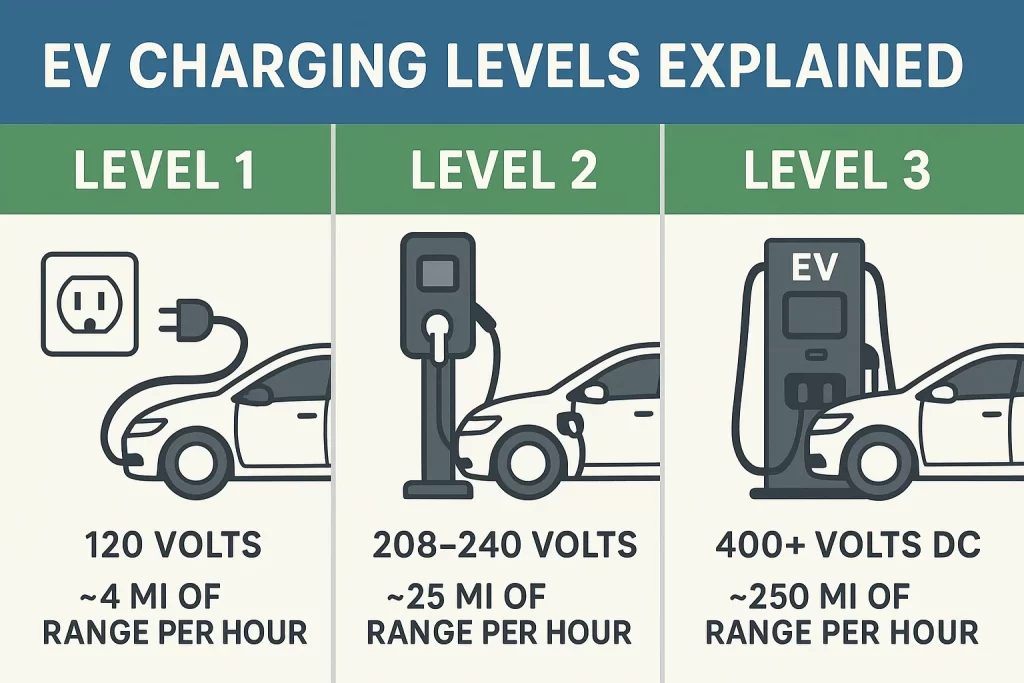
Electric vehicle charging is generally categorized into three main levels, which vary by power output and charging speed:
Power output: 1.3–2.4 kW
Speed: Adds about 3–5 miles of range per hour
Use case: Plugging into a standard home outlet
Best for: Emergency or overnight charging with no dedicated EV charger
Power output: 7.4–22 kW
Speed: Delivers up to 75 miles of range per hour
Use case: Common in homes, businesses, and public parking areas
Best for: Daily home charging or workplace EV infrastructure
Power output: 50–400 kW
Speed: Adds 173–298 miles of range in about one hour
Use case: Highway rest stops, commercial stations, high-traffic areas
Best for: Fast recharges during road trips or fleet operations
Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 stations that deliver AC (alternating current), Level 3 chargers convert grid AC into DC (direct current) before sending it to your vehicle. This bypasses the EV’s onboard charger, allowing for much faster charging speeds.
Because of this, Level 3 chargers are often referred to using various terms, including:
DC fast charging
Rapid charging
Ultra-fast charging
Quick charging
All of these refer to the same concept: high-power EV charging using direct current.
Here’s the technical breakdown:
The electricity from the power grid is alternating current (AC).
EV batteries can only store direct current (DC).
Level 3 chargers perform the AC-to-DC conversion outside the vehicle, using a built-in converter.
The converted DC is sent directly into the car’s battery, significantly reducing charge time.
Not all EVs support Level 3 charging. Most modern models do, but:
Some compact EVs or older models may be limited to Level 2.
Each vehicle has a max DC input limit. For instance, if your EV only accepts 50 kW and the charger supplies 350 kW, you'll only receive 50 kW.
Tesla drivers can use Level 3 chargers with the right adapter, although many prefer Tesla's proprietary Supercharger network.
Short answer: No.
Level 3 chargers require industrial-level power, far beyond what a residential electric system can provide. Most homes consume 30 kWh per day, whereas a Level 3 station can draw over 350 kW at once. For home use, a Level 2 charger remains the most practical and efficient solution.
Prices vary by provider, but you can generally expect to pay $0.30–$0.70 per kWh, or about $25–$50 per session. You're paying for:
Faster charging convenience
Higher installation and maintenance costs
Premium real estate usage (e.g., highway locations)
Also note that:
Some networks bill by minute, others by kWh, or both.
Membership plans can offer discounted rates or flat fees.
To avoid overpaying, make sure your car can take full advantage of the charger’s output.
The rapid rise of fast-charging infrastructure is essential to overcoming range anxiety—one of the top concerns for EV owners and prospective buyers. Faster charging:
Makes long-distance travel feasible
Reduces public charging congestion
Increases convenience for commercial fleet operations
However, while Level 3 stations are ideal for top-ups, daily home charging is best done with a Level 2 charger.
| Feature | Level 3 Charging |
|---|---|
| Power Output | 50–400 kW |
| Charging Time | 15–60 minutes (up to 80% charge) |
| Charging Type | DC (Direct Current) |
| Typical Locations | Highways, commercial hubs, public lots |
| Home Installation | Not feasible (requires industrial power) |
| Cost per Session | $25–$50 (varies by provider & speed) |
| Suitable For | Road trips, fleets, fast urban charging |
Level 3 charging is reshaping how we power electric vehicles. While not intended for everyday use, it plays a vital role in expanding EV infrastructure and supporting the global transition to clean transportation.